If you own cryptocurrency, you would at some point transfer them to another person. For your cryptocurrency transaction to go through safely, the protocol that you deploy for the transaction generates a series of cryptic numbers and letters — or in this case, “keys”.
Cryptocurrency keys are also used to verify the validity of cryptocurrency transactions — if A wants to transfer 10 BTC to B, both their keys must be the same. Otherwise, the transaction will fail.
Cryptocurrency keys take two forms: public keys, and private keys. Here’s how they work.
Public keys, explained
As its name suggests, a public key is a set of cryptographic messages that are shown to the public. A public key can be likened to one’s bank account number, and allows you to send or receive transactions. Public keys are used for encryption, i.e. converting a plain text to cipher text.
A cryptocurrency wallet is the hashed version of a public key; every public key is 256 bits long, whereas a wallet is 160 bits.
Private keys, explained
A user’s private key, on the other hand, is confidential. While anyone can view and access public keys, private keys must be kept secret from others. A public key can be likened to your account password; if anyone gains access to your private keys, they gain access to your cryptocurrency and spend them.
Your cryptocurrency wallet automatically generates private keys for you, and they are used for decryption, i.e. converting a cipher text to plain text in order to complete a transaction.
How do public and private keys work?
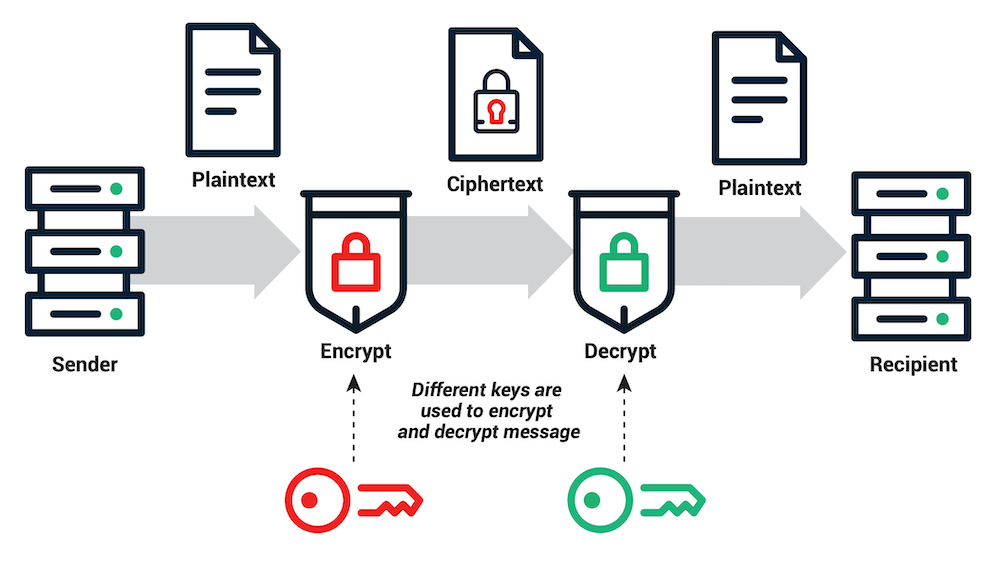
A public key is generated by a private key, and when two parties perform a transactions, their keys have to match it order for the funds to be transferred successfully. Here’s how it works:
- A wants to send 10 BTC to B. He obtains B’s public keys, which is recorded publicly on the blockchain.
- A encrypts the transaction data with B’s public keys and sends it over to B.
- B uses his private keys to decrypt the data sent to him by A.
- B now has the 10 BTC.
Methods to keep your private key safe

More than millions of dollars worth of cryptocurrency is stolen every year. According to data from Atlas VPN, as much as $3.78 billion was stolen from blockchain attacks in 2020, and wallet attacks were one of the most widely committed attacks.
Thus, it is crucial to keep your private keys safe in a cryptocurrency wallet. There are two main types of wallets to store your cryptos: hot and cold wallets.
Hot wallets are cryptocurrency wallets that are connected to the Internet and can be accessed via a desktop. Hot wallets automatically generate a public and private key after a user downloads it, and data is stored on your device’s hard drive.
Notable hot wallets include those provided by crypto exchanges like Coinbase, and digital wallet MetaMask.
Cold wallets are cryptocurrency wallets that come in the form of hardware, and are not connected to the Internet. Cold wallets typically come in the form of a USB stick, and keeping your private key safe can be as easy as writing down the English words that are generated from it.
Another type of cold wallet is a Ledger wallet. Ledger wallets are hardware cryptocurrency wallets made by Ledger, a company headquartered in Paris, France.
Ledger’s hardware wallets are device-based, which means they use storage mechanisms—USB drives—to store private keys, thereby making it difficult for hackers to access the key from an online location.
All Ledger products combine a Secure Element and a proprietary operating system that is designed specifically to protect a user’s cryptocurrency assets.
These wallets also use a 24-word backup recovery phrase that can be used to access a user’s cryptocurrencies if the device containing the private key is stolen.
Cold wallets are typically seen as the more secure option as it disconnects from any online activity and thus greatly lessens the risk of wallet attacks. However, traders that perform crypto transactions on a regular basis may still want to go for hot wallets for convenience.
Cryptocurrency Keys
Public and private keys are a crucial part of the crypto ecosystem, offering important lines of defence against blockchain attacks.
Choosing the best crypto wallet entirely depends on the individual’s needs, but regardless of which wallet you choose, make sure that you never share your private keys with anyone else!
Featured Image Credit: Ledger
Also Read: What Are Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) And How Do They Match Up Against Crypto?