Most people might be familiar with how to trade crypto on centralized exchanges (CEXs) such as Binance or Coinbase. Users who are more savvy with decentralized finance (DeFi) might also be familiar with decentralized exchanges (DEXs) such as Uniswap or dYdX.
But did you know about the different types of DEXs and how they work?
AirSwap started as the original peer-to-peer (P2P) DEX in 2017 by establishing over-the-counter (OTC) and request-for-quotes (RFQ) protocols for Ethereum. These swaps function differently from automated market maker (AMM) protocols used by Uniswap (and its many clones) and central limit order book (CLOB) protocol employed by dYdX (and other CEXs).
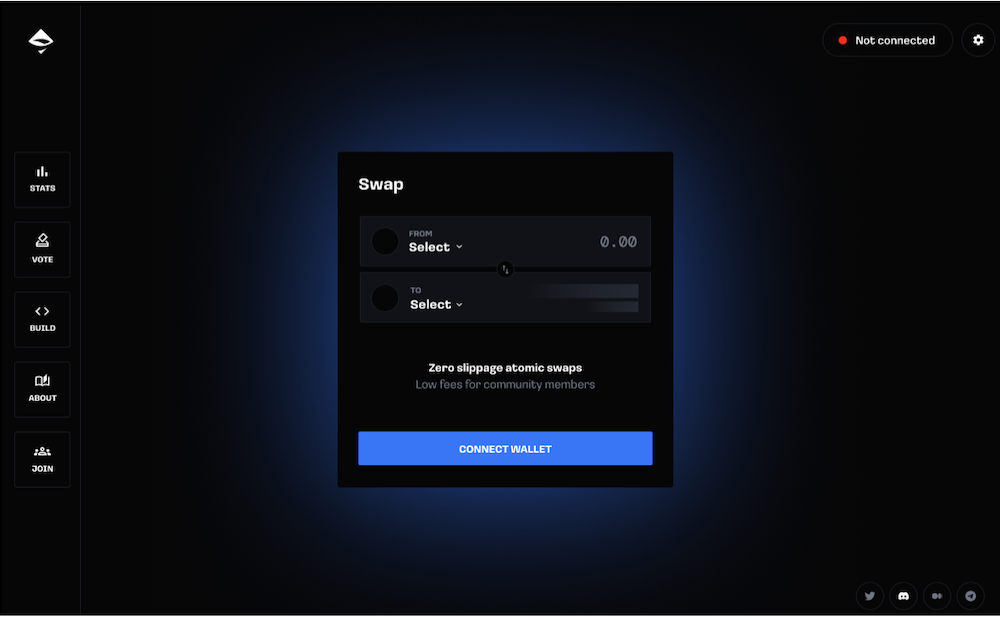
AirSwap recently celebrated its 4 year anniversary by launching its first open-source and community-built P2P DEX which includes support for gas free trades.
Read on to learn more about how AirSwap differs from other DEXs and how it helps to support communities in the metaverse.
A brief history of swaps
The earliest DEX, etherdelta, was built on a CLOB system. If you have ever traded on a CEX, the interface would be immediately familiar to you.
Users post orders to the system where a central order book then collates and matches orders between market participants. Like the name suggests, CLOB-based DEXs are not fully decentralized since it relies on a centralized order book to perform its matches.
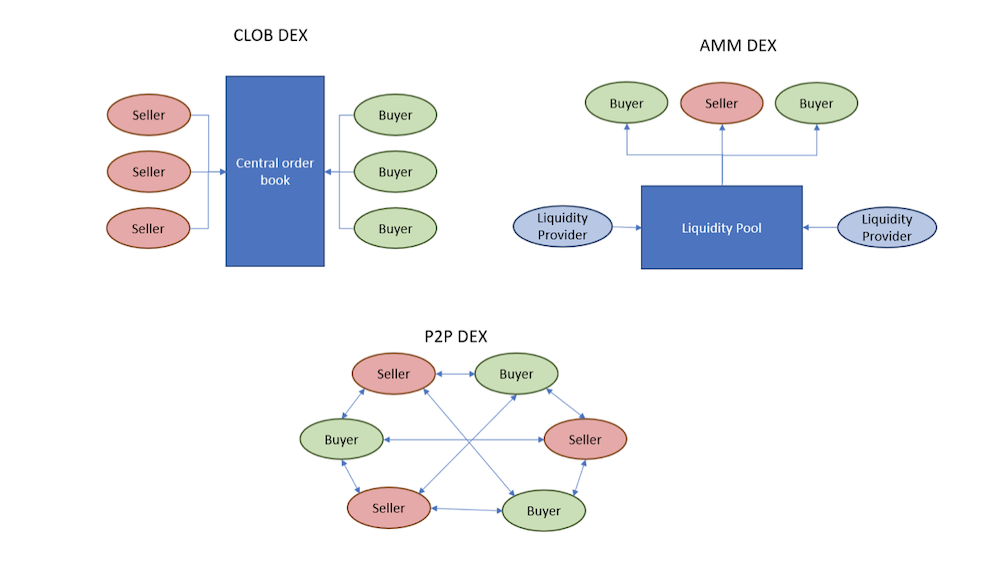
In contrast, AMMs operate by allowing anyone to deposit liquidity into its contracts. Instead of matching buyers and sellers, both buyers and sellers trade against a common liquidity pool which is formed by liquidity providers.
Liquidity providers earn fees levied on each swap, but in return, hold the risk of market movements (commonly known as impermanent loss).
What problems does AirSwap solve?
Aside from its partially centralized nature, CLOB protocols tend to be very gas inefficient as traders would need to spend gas to post or cancel orders made to the order book. Notably, the most popular CLOB-based DEX, dYdX, runs on an Ethereum L2 to avoid the high gas fees charged on mainnet.
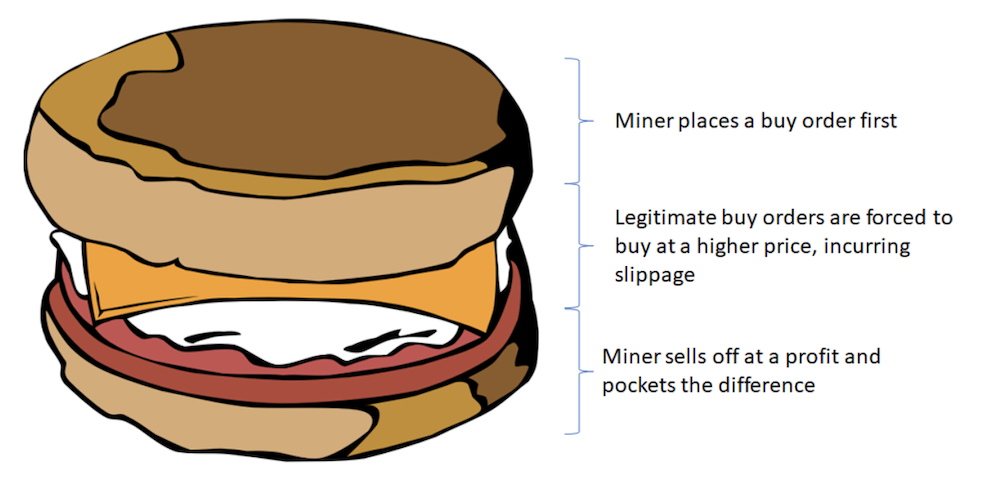
AMMs, on the other hand, are easily attacked by what is termed as miner extractable value (MEV). Since the exact exchange rate of an AMM is only determined at the time of settlement, users would not be able to know in advance exactly how many tokens he would receive from the swap, since the transaction would take some time to be executed on the blockchain.
The difference between the quoted and executed price, termed “slippage”, could be exploited by miners who ultimately determined the orders by which transactions are arranged in a block.
For example, if a miner saw a large trade swapping ETH for USDC coming through, he could effectively sandwich the order with a buy and sell order which causes the trader to buy at a slightly higher price, while the miner pockets the extra profit.
In addition to the above, CLOBs and AMMs are not suitable for all types of swaps. Take the case of NFTs for example. Swapping NFTs cannot be performed by these DEX protocols. Some projects may also choose to sell their tokens at a fixed price or keep trading within their own community, and global liquidity protocols might not be the most effective setup for such projects.
How does AirSwap work?
AirSwap is uniquely built around OTC and RFQ protocols. Using AirSwap’s atomic swap contract, there is no risk of the counterparty backing out of the trade after taking your funds. The entire swap is governed by the smart contract, and either both parties make the trade, or the entire transaction fails and funds are returned.
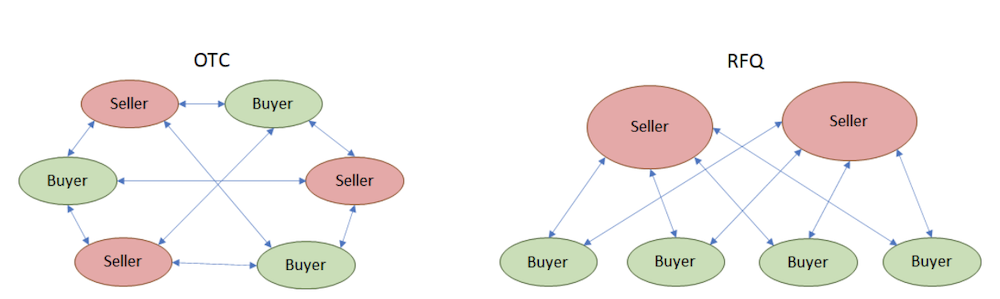
OTC and RFQ protocols are two ways in which peer-to-peer swaps can be made.
OTC swaps function more effectively in a “many-to-many” marketplace, where there are roughly the same number of buyers and sellers. OTC swaps are matched manually and an active social community is required for matches to be found on both sides.
On the other hand, an RFQ system is more efficient in a “few-to-many” marketplace, where a few suppliers provide liquidity for many members of the community.
In an RFQ marketplace, liquidity providers can set up servers or delegate smart contracts to automatically serve liquidity to the rest of the community.
This could be due to a central liquidity provider (e.g. a community treasury) or several community members who are more active in providing liquidity to the marketplace.
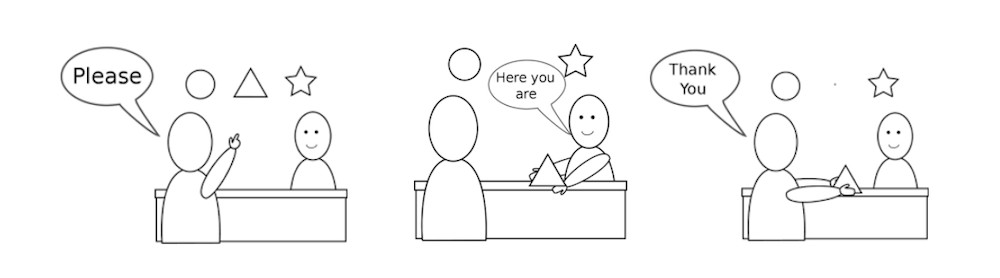
Most people should already be intuitively familiar with these systems in real life. In an OTC swap, two parties sign an agreement to trade their tokens at a fixed price. This is no different from going to a store to buy an apple. You ask the shopkeeper how much the apple costs, he tells you it’s a dollar. You agree and hand over $1 to the shopkeeper and he hands you back an apple. No other complicated procedures involved.
RFQ systems should also be familiar to many people. For example, when hunting for a contractor to renovate your house, you would go around to different vendors to get quotations for their service. After comparing a few quotes, you might pick the cheapest one, or maybe the one who can provide you the best value for money.
The simplicity of such transactions make them very intuitive to use. There is no way to front-run the transaction since counterparties are specified and prices are settled prior to the execution of the swap. What you see in the quote is exactly what you would receive – no slippage at all.
Now introducing… gasless swaps!
Last Look (LL) is a new AirSwap protocol that is very similar to RFQ but with huge implications for swaps. The main advantage of the protocol is that the user does not need to cover the gas fees of submitting the transaction. Instead, the market maker prices the gas fee into the quote and pays for the gas of the transaction.
This means that it is now possible for anyone to carry out a swap without owning any ETH. Last Look simplifies swapping greatly, at one glance anyone can see exactly how much they will receive for the swap. No more fumbling to get ETH to cover the transaction costs.
Why AirSwap?
AirSwap for AirSwap
AirSwap is first and foremost a community of developers. The AirSwap community funds active development of the DEX and in turn, fees accrued from the DEX is distributed to contributors and community members.
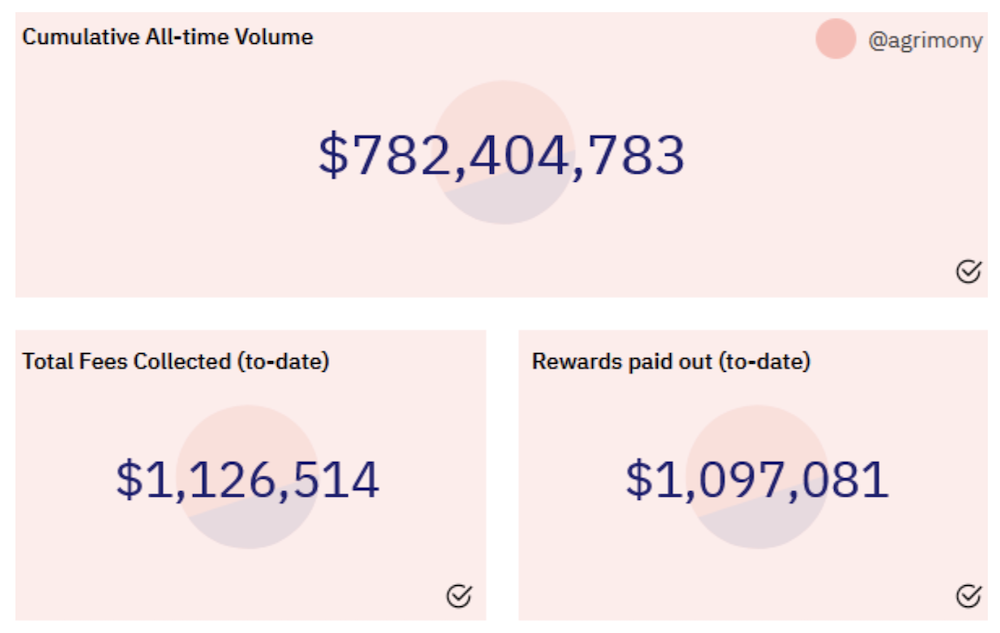
Since the beginning of the year, close to $800M of volume has passed through AirSwap, generating more than $1M in protocol fees for community members.
There are also other benefits to being part of the AirSwap community. The community continuously finds ways to improve the AirSwap ecosystem.
For example, a proposal to implement a fee discount for members was passed recently. Additional utility and value is thus created by the community, for the community. Contributing to AirSwap is a positive feedback cycle where the community wins together.
AirSwap for Institutions
Institutional traders can use AirSwap’s OTC protocols to make their swaps without worrying about MEV and sandwich attacks. The trader knows ahead of time the exact amount he will receive from the swap.
In addition, the trader will also know the exact address of the counterparty. This means that institutions can implement whitelists to only trade with trusted counterparties.
AirSwap RFQ is also the best protocol for traditional market makers to participate in DeFi by running their trading strategies on RFQ servers. Institutional traders are easily able to set up trading servers to supply liquidity to DeFi markets in order to tap in on the burgeoning DeFi ecosystem.
AirSwap for NFTs
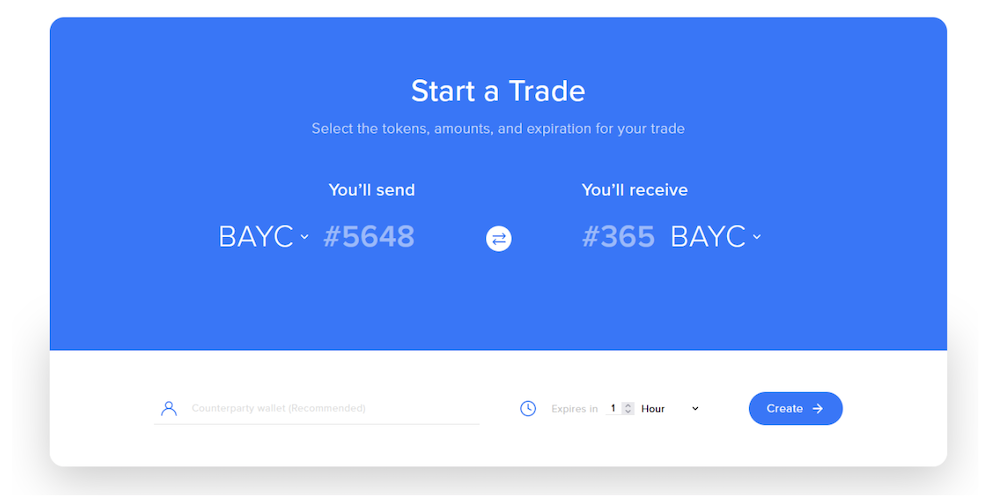
AirSwap’s OTC protocol is perfectly suited for NFT swaps. Since NFTs are non-fungible, traders are typically interested in swapping for a specific token rather than a type of token.
Using AirSwap, traders would be able to specify an NFT they would like to purchase, and a corresponding token they would like to trade for it. There is built in support for both ERC-20 and ERC-721 standards, which means that AirSwap natively supports NFT to NFT swaps.
Imagine being able to bid for an NFT using any token such as ETH, USDC or even a totally different NFT!
AirSwap for the Metaverse
As we enter the metaverse, virtual communities become the primary reality. These social communities (commonly structured as decentralized autonomous organisations or DAOs) need a good way to interact and allocate resources within members of the DAO or between closely aligned DAOs.
For example, a teacher of an online classroom might want to create a social DAO that incentivizes learning. Students can earn DAO tokens by participating during the class, or by submitting correct answers during tests.
Students may even be able to reward their peers in peer-learning programs or allocate tokens among group members who participate in group projects. These DAO tokens could then be traded in for NFT rewards according to each student’s grades at the end of the term.
AirSwap enables liquidity of such social tokens, where DAO tokens can be swapped in an internal DAO marketplace. This allows efficient trading of social token liquidity where deep liquidity pools are not required (or even wanted!). AirSwap empowers communities, big and small, to be part of the metaverse by enabling frictionless trades within and between these metaversal societies.

AirSwap for the Future
Since AirSwap transitioned into a DAO at the beginning of the year, more than 20 AIPs (AirSwap Improvement Proposals) have been voted in and implemented by more than 20 contributors.
AirSwap has also been implemented by Metamask Swaps since Oct 2020 and is tracking to break $1B+ in volume by the end of 2021 – an increase of 20x since 2019!
The launch of the new AirSwap DEX marks the first product designed and delivered by the community. The community continues to ideate, design and deliver new improvements to the protocol and platform. The new DEX-DAO setup has proven to be a sustainable way of attracting new open-source contributors to the platform, allowing anyone to begin building with AirSwap.
With so many opportunities for growth, AirSwap is uniquely placed to be a key pillar of the future web3 metaverse. Currently, AirSwap is working towards bringing its swapping protocols to other chains in order to serve the needs wherever they might be. As it continues to grow, AirSwap is a project worth keeping an eye out for.
Check out the newly launched AirSwap DEX here.
Featured Image Credit: Chain Debrief
Also Read: VeChain: How It Disrupts Supply Chains with Blockchain Technology