The latest tech buzzword being bandied about – Web 3.0.
It has become such a hot topic in recent times and almost everyone in the community talks about it.
But what exactly is it?
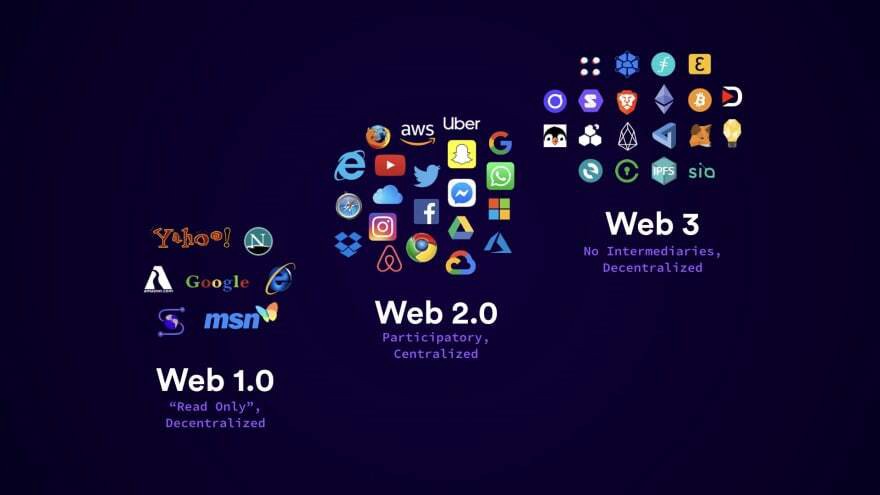
Before we understand what Web 3.0 is, it’s important to take a look at what Web 1.0 is as well as its predecessor Web 2.0 that was created in 2015.
Web 1.0
Web 1.0 was the first stage of the World Wide Web revolution, usually referred to as a read-only web. Websites were informational and contained only static content. The main use of the Internet was hyperlinking and book marking to web pages.
Users on the Internet were consumers of content created by content creators in the era of Web 1.0 from 1991 to 2004.
A flaw of Web 1.0 was that there was no connection between user and producer.
Web 2.0
Then came Web 2.0 which existed from 2004 up till present. It is the second stage of the World Wide Web revolution, referred to as a read-write web as described by Berners-Lee. In Web 2.0, emphasis was given to user-generated content, ease of use, participatory culture and interoperability.
Advantages
- Ease of usage
- User friendly
- Available at any time, any place
- Current information
- Real time discussion
Disadvantages
One disadvantage of Web 2.0 is that the content quality is low as authenticity is not always verified.
Another major flaw of Web 2.0 is that all data is stored on a centralised server which is controlled by the companies.
Facebook, Google, and Twitter began storing users data in their servers in order to serve us better content through an algorithm designed to track our activity. This resulted in an increased stay on their websites, which provided a higher ad revenue for these companies.
These companies eventually started selling our information to advertisers, which only meant more money for them.
In summary, we can say that users are the product in Web 2.0.

Web 3.0
So what is Web 3.0 and why is everyone talking about it?
Web 3.0 was created in 2014 by Gavin Wood, an English computer scientist who co-founded Ethereum and is also the creator of Polkadot and Kusama.
The Web 3.0 concept aims to create a decentralised and secure Internet where people can securely exchange money and information, without the need for an intermediary.
Web 3.0 applications either run on blockchain/s or peer to peer nodes as compared to Web 2.0 where data is stored in a single database or on a cloud provider.
Concept
Bloomberg has described Web 3.0 as an idea that “would build financial assets, in the form of tokens, into the inner workings of almost anything you do online”.
Some visions are based around the concept of Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs).
Decentralised Finance (DeFi) is another key concept of Web 3.0. DeFi allow users to exchange currency without needing a bank or the government.
Also Read: Introducing Defi 2.0: Exploring The Hype Behind The New Wave of Decentralised Finance
Advantages
- Data ownership:
As mentioned above, companies control and exploit user-generated data in Web 2.0. In Web 3.0, users have full ownership of the data. You will be able to choose what information you want to share with businesses and advertising companies. - Transparency:
The decentralised web enable users to track their data. Stakeholders will always be aware of the value and commerce they are associated with. There is no need to rely on a middleman for access to this data. - Lesser Intermediaries:
One of the aim of Web 3.0 is to connect companies directly with customers. With that, there will be almost zero central authorities that will receive a cut from the electronic transactions that take place. - Uninterrupted Services:
In Web 3.0, data will be stored on distributed nodes. Thus, users will not have to think about any service disruptions due to technical or other reasons. - Personalised Experience:
Web 3.0 is able to offer a more personalised Internet surfing experience as websites can better identify user’s preferences. Web applications analyse our internet usage and habits to customise themselves to fit best to our device, location, etc.
Disadvantages
- Regulations:
As Web 3.0 is build around the narrative of decentralisation, it is difficult to monitor and regulate activity. This could result in a rise in cybercrimes. - Privacy:
Transparency has its downside too – privacy. User’s personal and public data becomes easily accessible as Web 3.0 is huge and interconnected, which is why it is easier for anyone to gain access to the data you choose to share online. - Complexity:
Beginners may find it challenging to understand the complicated Web 3.0 concepts.
Closing thoughts
It can be a double-edged sword creating a decentralised social media platform where users can add data but do not have the option to erase it.
It is a fundamental human right to have the freedom of speech however, this may come at the expense of users publishing explicit content that cannot be deleted by anybody. This can be highly dangerous as it may unintentionally harm innocent parties.
There are many different perspectives on what Web 3.0 is – some believe it is a hoax created by cryptocurrency traders, while others believe it can be game changing. In my opinion, we are in early development stages and still have a long way to go before we can achieve what we set out to achieve.
What do you guys think? Is Web 3.0 just a buzzword or is it actually happening?
Featured Image Credit: CoinMarketCap
[Editor’s Note: This article does not represent financial advice. Please do your own research before investing.]
Featured Image Credit: Chain Debrief
Also Read: Want To Be A Crypto Investor? Here Are 10 Resources To Get Yourself Up To Speed In Web3