Ethereum’s Shanghai upgrade, slated for March this year, will come with a number of improvements for Web3’s oldest Smart-Contract enabled blockchain. Most importantly, Shanghai will begin to allow users to withdraw staked Ether as well as any accrued rewards from staking pools.
Ahead of the upgrade, the hard fork will be implemented on both the Sepolia testnet and the Goerli testnet before being ready for the actual Ethereum blockchain, ensuring that the transition can be done seamlessly for both users and validators.
Also Read: Are Liquid Staking Derivatives The Solution For Ethereum’s $19B Withdrawal?
Could The Shanghai Upgrade Be Pushed Back To April?
For withdrawals to occur, the Ethereum Network needs to go through a total of two hard forks. Christened “Shapella”, this transition will include both the Shanghai and Capella hard forks, which will affect the execution and consensus layers respectively.
Sepolia testnet has successfully upgraded to Shapella! 🌃
— terence (@terencechain) February 28, 2023
Some of the Prsym validators are offline due to the old geth version. They will come online in the next 10 mins!
Next stop: Goerli pic.twitter.com/pb43Gq7w9C
However, for Ethereum to fully transition, it will require one more testnet, Goerli, to undergo the same process.
During the merge, upgrades to both testnets were done within a two-week timespan, due to the urgency implemented by the “difficulty bomb”. The merge finally occurred almost exactly one month later, on the 6th of September 2022.
Following this timeline, we would expect that the Shanghai upgrade will only come sometime in April, but could even be delayed into the latter half of Q2 this year should there be hiccups.
Preparing Yourself For The Shanghai Upgrade
As it takes 32 Ether to run a validator node by yourself, many users would choose to either stake on a centralized exchange or participate in a Liquid Staking Derivatives such as Lido Finance.
With more than 13% of $ETH supply, or approximately $26 billion at the time of writing, being staked right now, this could be a point for worry as users believe a mass withdrawal of $ETH could lead to a sudden dump in prices.
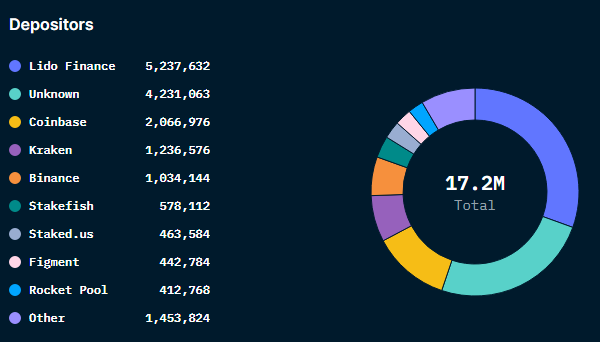
Thanks to on-chain data analytics platform Nansen, we can see that almost 30% of staked Ether is in the liquid staking platform Lido finance, meaning that users can already sell the receipt token for their $ETH should they need liquidity.
➡️ Full Withdrawals – Assumptions
— korpi (@korpi87) February 7, 2023
– Validators exit asap – every day max number of exits is processed (1800)
– Every day all FW are processed (1800)
– The number of active validators stays flat – new ones are set up
– Staker category and profitability defines willingness to sell https://t.co/VhAIveBkxh
Furthermore, only 43,200 $ETH or 0.27% of all staked $ETH can be withdrawn every day due to mechanisms implemented by the Shanghai upgrade.
For users who currently stake their Ether on centralized exchanges, these CEXes will often provide you with a liquid-staked version of your token, such as $cbETH on coinbase. However, many CEXes have yet to announce their plans for $ETH staking withdrawals outside of these receipt tokens.
For users who have staked their $ETH with validators, you can either partake in a partial withdrawal, redeeming $ETH accrued over the 32 Ether benchmark and continue to participate in network consensus, or fully liquidate your current stake, subject to delays in the withdrawal queue.
The Shanghai upgrade, which includes EIP-3651, EIP-3855, and EIP-3860, will also helps users save fees on certain processes, such as no longer having to pay fees on failed trades.
What Will Ethereum Look Like After The Shanghai Upgrade?
As users are finally able to withdraw their staked Ether, it seems that the transition to proof-of-stake will finally be complete.
However, this is but one step in Ethereum’s long-term goal of solving the blockchain trilemma of decentralization, security, and scalability.

The next stage for Ethereum will be “The Surge”, which will introduce sharding to the Ethereum network, and aims to allow the Layer 1 to process 100,000 transactions per second, a far cry from its current state of ~15 TPS.
Vitalik Buterin, Creator of Ethereum, also notes that Ethereum’s approach to scaling will be based on “proto-danksharding”, where individual blocks will processed solely by one block builder, as opposed to typical sharding, which requires multiple builders.
Also Read: Comparing Arbitrum And Optimism, Which Is Better?
[Editor’s Note: This article does not represent financial advice. Please do your research before investing.]
Featured Image Credit: ChainDebrief