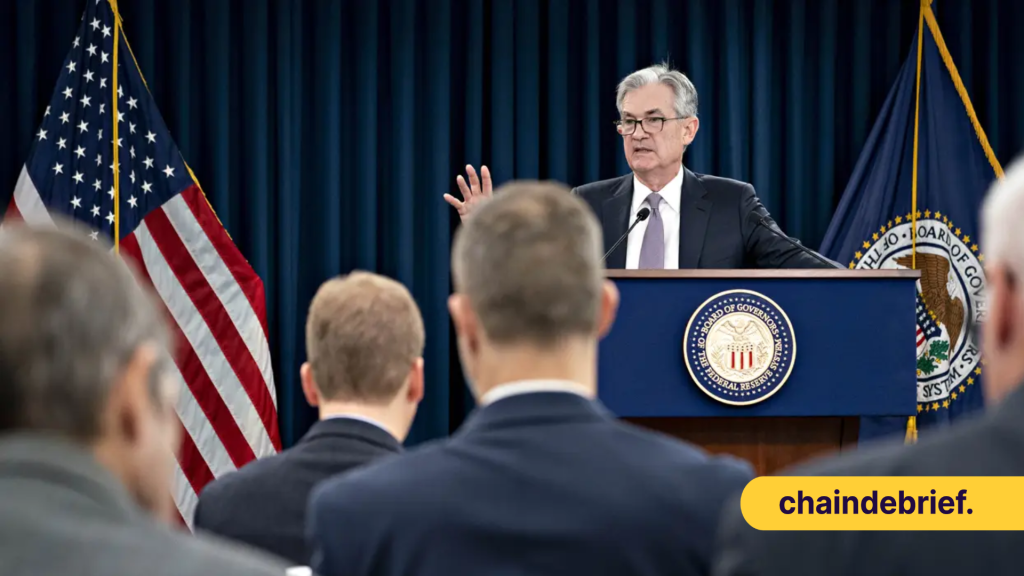
What impact does FOMC conducted by the Feds have on the crypto market? Before we delve deeper into its implications and economics, we first have to understand what FOMC and Federal Reserve mean.
FOMC
Also known as the Federal Open Market Committee, FOMC meetings are held eight times a year (roughly every six weeks) and comprise 12 members–the seven members of the Board of Governors and five of the 12 Reserve Bank presidents.
Their main purpose? To conduct policy by adjusting the level of short-term interest rates in response to changes in the economic outlook. That’s where you hear the familiar term, interest rate hikes.
Federal reserve
The “Fed” is the central bank of the United States, which in its own words “, provides the nation with a safer, more flexible, and more stable monetary and financial system.”
It is also noted that the decisions made by the Fed do not need to be approved by Congress or the president. However, they consult other avenues of the government through congressional testimony, sharing forecasts and publishing a wide range of research products on regional and national economic issues.
They have three primary functions:
- Managing the nation’s monetary policy by overseeing the money supply and adjusting interest rates;
- Providing and maintaining an effective and efficient payments system between financial institutions; and
- Supervising and regulating banking operations.
How does it affect cryptocurrency?
Recently in June, it was released by the Fed that inflation numbers saw an all-time high of 9.1%. Why is this inflation statistic important? Well, it is a benchmark in determining the actions taken by the Fed in raising interest rates to combat inflation during the FOMC meeting.
Cryptocurrency has often been touted as a cure-all for what ails you, be it inflation, low-interest rates to the devaluation of fiat currency.
All of those were easy to believe in, especially in a bull market, but the winter revealed a side of crypto we need to be wary about.
But why does high inflation matter to crypto?
Imagine taking a 10-year loan to buy a $24,000 car with a bank charging 5% interest monthly. That would mean paying $24,000/10 = $2,400 a year and $2,400/12 = $200 each month. In addition of the 5% monthly interest, your total monthly payment for the car loan would be $200 + ($200*0.05) = $210.
When the feds raise the increase rates to 10%, the total monthly payment will increase to $200 + ($200*0.1) = $220. It makes it more expensive to take up the loan in the first place as you now need to pay a higher instalment fee, discouraging you from spending as the cost of borrowing now increases.
People would now instead save than invest in a high-interest rate climate. They will withdraw their investments in riskier assets to “safer” investments like government bonds with risk-free rates. With high inflation rates, investors are also unlikely to hold cash.
As investors shift away from high-risk crypto assets, the demand value of crypto assets will fall, causing their value to spiral into a downtrend.
Tech stocks in the particular struggle against interest rate hikes and the growing correlation between crypto and equities are not helping the cause of Bitcoin being a hedge against inflation. The backlash of these effects will also be reflected in crypto prices as investors view bitcoin as a “risk on” asset.
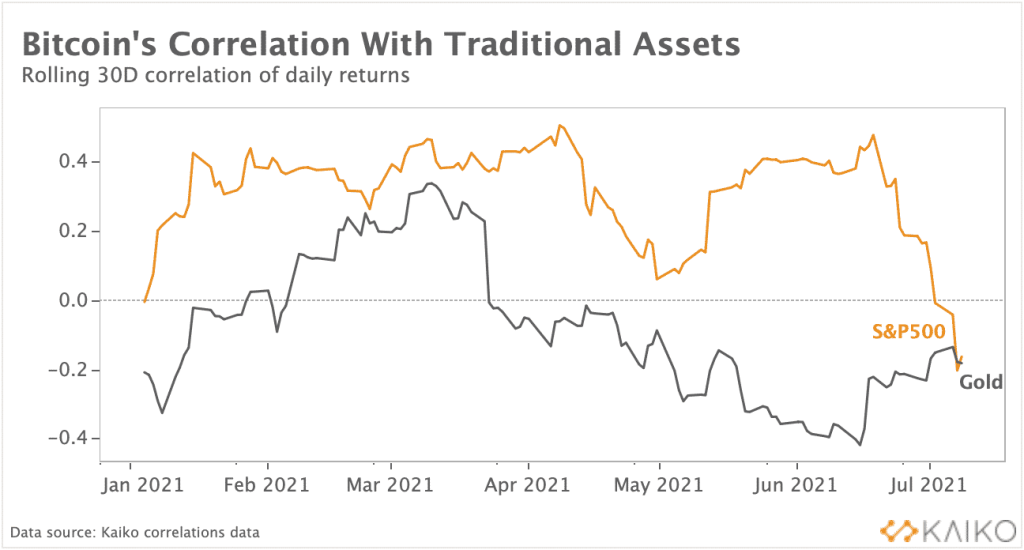
In the short term, that might not necessarily be a good thing. When inflation is persistently high, investors look for areas to maintain their cash flow. However, with the volatility of crypto, being afraid of how long recovery will be, the shift in investment outlook to risk-off assets is a more pronounced move to take.
As the market expects inflation to stay above the Fed’s target, the central bank will continue to hike interest rates throughout the year. And where do you find out about the latest interest rates imposed on the economy? You guessed it, the outcome of the FOMC meeting.
History of FOMC and the price of Bitcoin
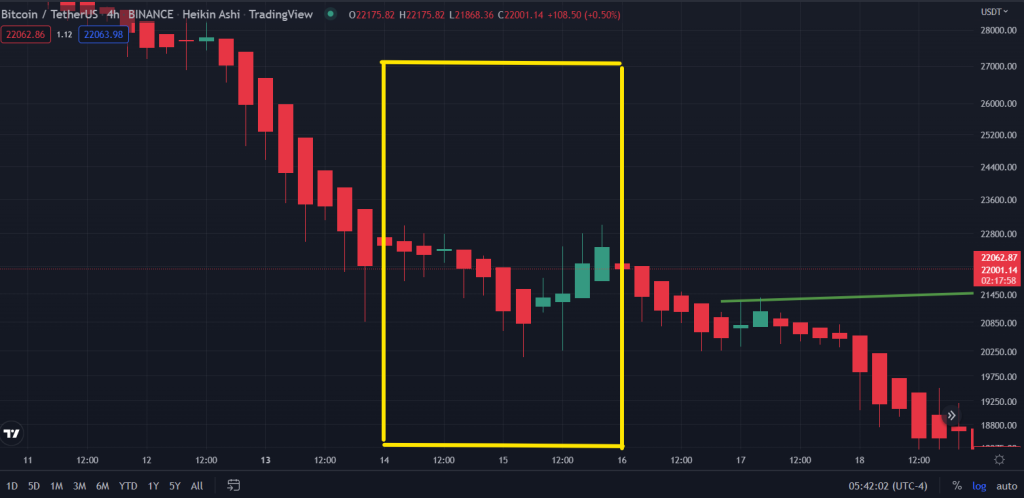
26-27 Jan 2022
(FOMC minutes summarised and extracted from TheBalance)
“The FOMC maintained its target for the FFR at a range of 0% to 0.25%, which had remained the target goal since the spring of 2020.8 However, due to improving labour market conditions and a high rate of inflation, the FOMC said it expected to be able to raise the federal fund’s target range soon. It continued its quantitative easing program. The Committee decided to reduce the monthly pace of its net asset purchases to end them altogether by early March. The Committee also decided it would increase holdings by $20 billion per month for Treasury securities and $10 billion per month for agency mortgage-backed securities.9.”
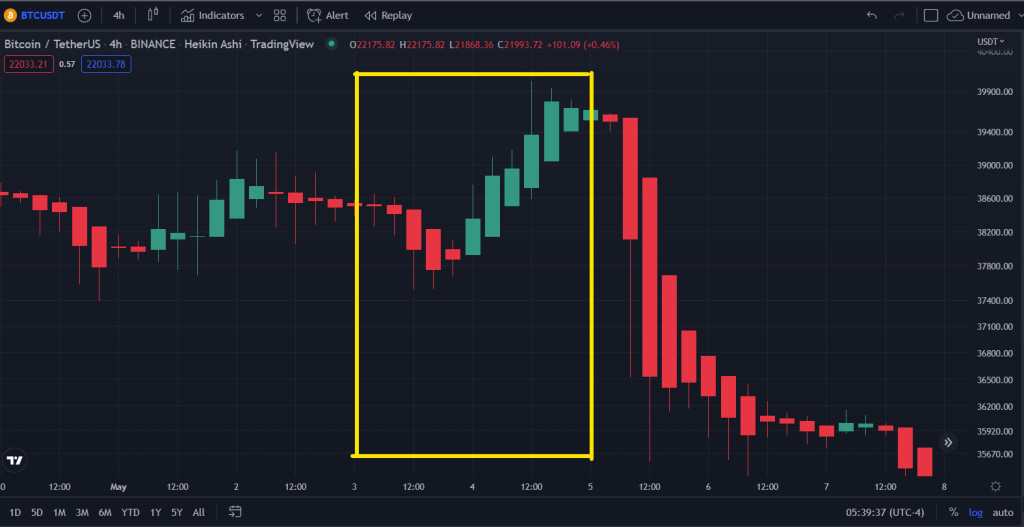
15th-16th March 2022
(FOMC minutes summarised and extracted from TheBalance)
“The FOMC raised its target for the FFR to 0.25% to 0.50% and said it anticipated further rate hikes while also reducing holdings accumulated during its quantitative easing (QE) program.6“
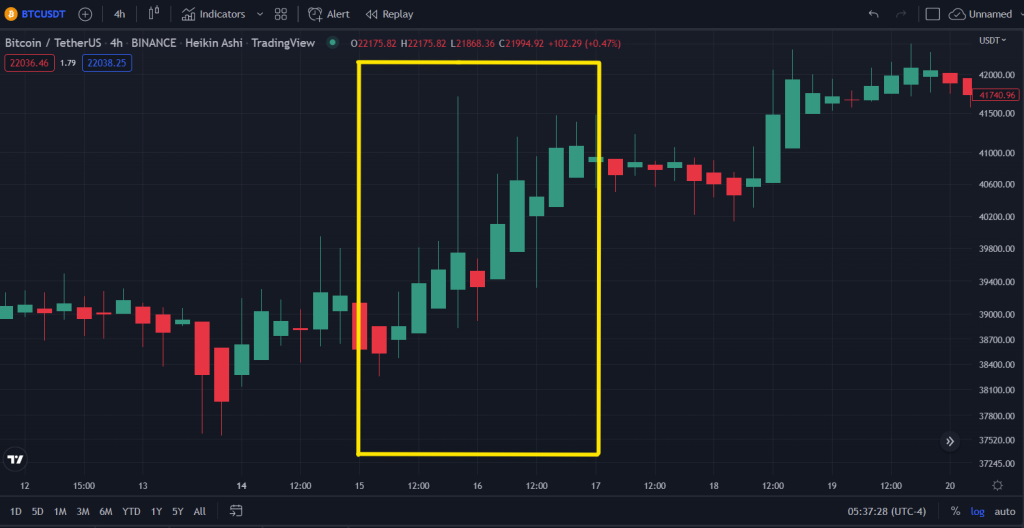
3rd-4th May 2022
(FOMC minutes summarised and extracted from TheBalance)
“The FOMC raised its rate by 0.50% (50 basis points), moving its target for the FFR to 0.75%-1.00%. The Fed stuck to its projection of 5 additional increases to the FFR in 2022.”
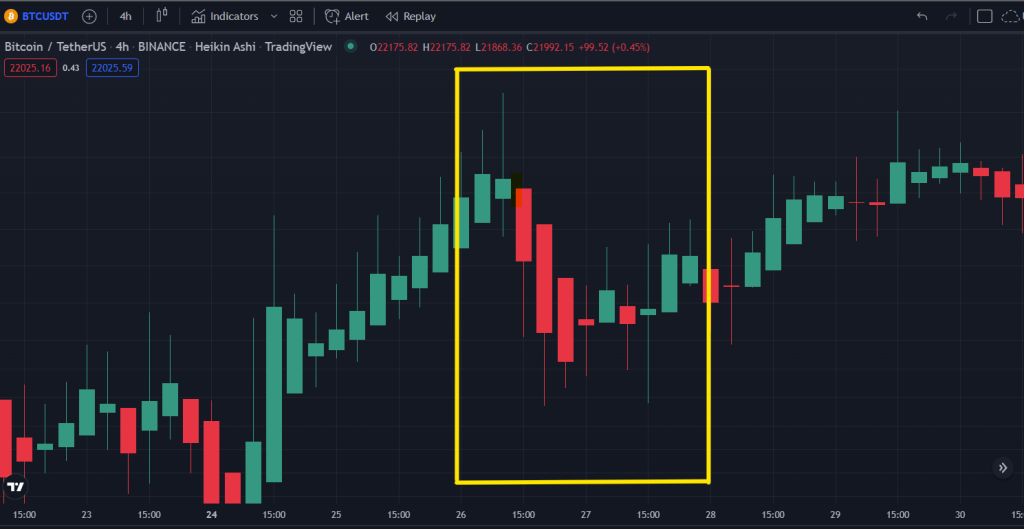
14th-15th June 2022
(FOMC minutes summarised and extracted from TheBalance)
“The FOMC raised its rate by 0.75% (75 basis points), moving its target rate for the FFR to 1.50%-1.75%. The increase passed in a vote of 10-1. The FOMC also downgraded its economic projections. The FOMC stated it was “strongly committed” to returning inflation to its 2% objective, perhaps inferring it would continue to act aggressively until inflation started to come down.7“
Beginner-friendly economic summary
The effects of (some examples) covid relief packages and supply shock caused by the Ukraine and Russia war imposed the FED to roll out various monetary policies. Monetary policies introduce new money into the economy and increase inflation.
To combat inflation, the FED would increase interest rates in the short term to decrease economic spending. Demand for products and services is expected to fall as borrowing becomes more expensive and people spend less due to a liquidity crunch.
The reduction in spending is also likely to cause a decrease in investing.
When the FOMC has been dovish or cuts rates — the daily abnormal return has been positive. When the FOMC has been hawkish or increased rates, the daily abnormal return on that day is usually harmful.
Although not every rate cut ( or hike) is associated with an unusually high (or low) return. There’s some evidence for longer-term effects as well, given that weekly abnormal returns have been positive on easing monetary policy.
Closing thoughts

Activity in crypto has slowed down significantly; expert says it is a result of investors taking risk-off assets suitable for the noise in the microenvironment. However, the prospect of higher inflation shortly favours bitcoin.
At the same time, the crypto-asset is becoming recognised by institutional investors as an insurance policy for the current state of economic affairs. While the price of bitcoin was mainly driven for many years by internal events, macroeconomic events are becoming more critical, with the leading cryptocurrency increasingly assuming the role of a barometer of the state of the global economy.
[Editor’s Note: This article does not represent financial advice. Please do your own research before investing.]
Featured Image Credit: BankRate
Also Read: Inflation Rises To 9.1%, Making Sense Of How It Affects The Crypto Market