Since Ethereum’s creation, scalability has been a significant issue. Ethereum developers and researchers are always looking for new methods to increase the network’s capacity.
Plasma was one of the most successful, substantial, and promising Layer 2 solutions for Ethereum scaling until a few months back. Also, Truebit and State Channels were viable alternatives.
Rollups and other options like them have recently taken up the market share.
Types of Rollups
Rollups are amongst the most promising types of Layer 2 solutions, and they are becoming increasingly popular. However, because these solutions offload transaction calculations to a third-party server and store transaction data on the Ethereum blockchain, rollups are protected by Layer 1.
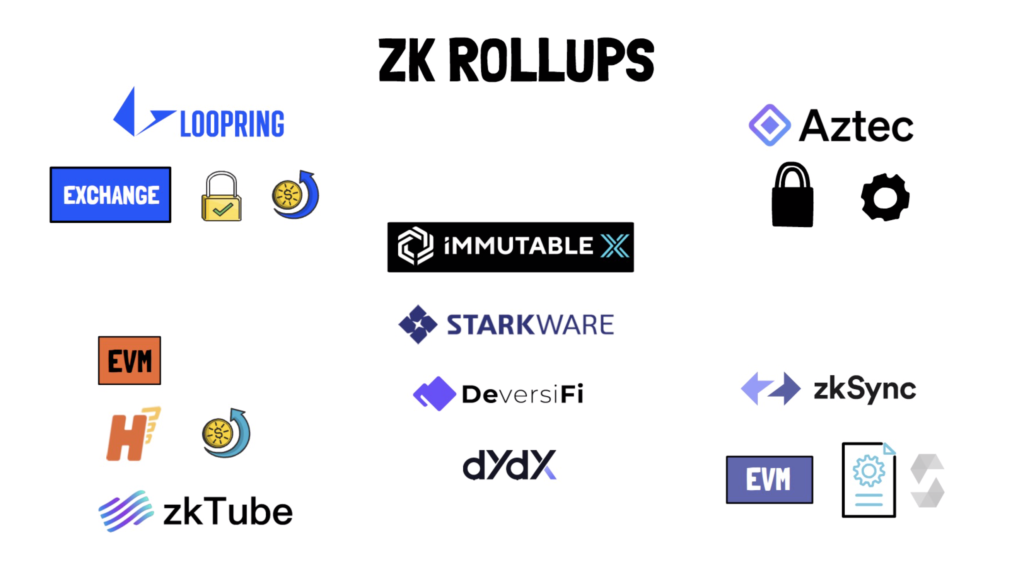
Rollups are available in two different varieties: Zero-Knowledge (ZK) and Optimistic.
Between the two forms of rollups — ZK rollups and optimistic rollups — the process of verification is the most crucial difference.
In the case of ZK rollups, cryptographic proofs are generated that may be used to validate the legitimacy of transactions. Validity proofs are generated for each batch of transactions and sent to the main chain for validation.
What is a ZK Rollup?
ZK Rollups rely on Zero-Knowledge Proof for all state transitions to function correctly. Afterwards, each transaction is compared to the smart contract on the mainchain.
Zero-Knowledge Proof protects all state transitions, which ensures that no invalid transactions or malicious contracts can be executed because everything must be validated against the smart contract before it can be implemented.
A ZK Rollup has the advantage of being significantly quicker than an Optimistic Rollup since it is considerably lighter on Layer 2 because the validation occurs on the mainchain rather than on the sidechain. Because mainchain validation occurs almost instantly, ZK Rollups are quicker and more scalable than previously.
ZK Rollups have a maximum transaction rate of 2000 transactions per second because all of the validation occurs on the sidechain.
It’s vital to highlight that the speed differential isn’t significant in human perception. However, in terms of computational performance, there is a considerable disparity.
What is an Optimistic Rollup?
Optimistic Rollups depend on a user submitting a new state root to the sidechain without validating the Rollup contract.
That’s correct; the contract does not do any verification. But the others can witness every transaction on the L1 and will invalidate a malicious state root if they so choose.
In our perspective, the difficulty with Optimistic Rollups is that they take a bit longer to validate since they rely on smart contracts at the second layer. As a result, Optimistic Rollups are less scalable than ZK Rollups in scaling.
Optimistic Rollups vs. ZK Rollups
ZK Rollups will most likely win the Rollup war. However, both will likely coexist in the future.
This complicates matters since some DeFi programs utilize Optimistic Rollups while others use ZK Rollups, making it more difficult to communicate between them.
Tether has already begun employing ZK Rollups in an effort to alleviate congestion on the Ethereum blockchain. Therefore, it seems probable that ZK Rollups will prevail. Tether, the largest cryptocurrency stable coin, and an ERC-20 token are for people who don’t know.
Tether’s congestion on the mainchain is heartening to know that ZK Rollups are being used to alleviate it.
ZK Rollups are also more efficient than Optimistic Rollups in transaction rate. Although zero-knowledge proofs take more computer resources than other options, ZK Rollups allow ten times as many transactions as Optimistic Rollups. This is the only drawback we can find with ZK Rollups.
Final thoughts
Layer 2 rollups are among the finest and may even be better than the other options in some cases. However, both of these techniques are still in their development and haven’t been adopted by many DeFi initiatives.
Optimistic Rollups will be less popular with DeFi projects than ZK Rollups. On the other hand, it may take some time and congestion on the network for ZK Rollups to be widely adopted on DeFi.
Featured Image Credit: Chain Debrief
Also Read: What Is The Ethereum Name Service (ENS) And How Does It Work?